Understanding A1c Levels: An Essential Guide for Diabetic Patients
Living with diabetes requires careful management of blood sugar levels to ensure optimal health. One critical tool used by healthcare professionals to monitor diabetes is the A1c test, also known as the hemoglobin A1c test. This test provides valuable insights into an individual’s average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months.
The Importance of A1c Testing
 The A1c test reflects the percentage of hemoglobin in the blood that has glucose attached to it. Hemoglobin is a protein found in red blood cells that carries oxygen. As red blood cells have a lifespan of approximately three months, this test offers a comprehensive view of long-term blood sugar control.
The A1c test reflects the percentage of hemoglobin in the blood that has glucose attached to it. Hemoglobin is a protein found in red blood cells that carries oxygen. As red blood cells have a lifespan of approximately three months, this test offers a comprehensive view of long-term blood sugar control.
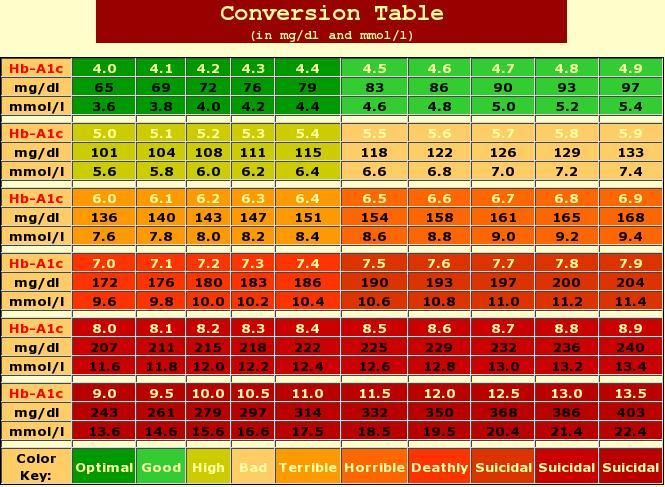
An A1c level below 5.7% is considered normal for individuals without diabetes, while a level between 5.7% and 6.4% indicates prediabetes. Diabetic patients typically strive to maintain an A1c level below 7%, although individual targets may vary depending on personal circumstances and healthcare professional recommendations.
Interpreting A1c Levels
 A1c levels are typically presented as a percentage, but they can also be converted to average blood glucose (sugar) levels, providing patients with a better understanding of their daily fluctuations. For instance, an A1c level of 7% corresponds to an average blood glucose level of approximately 154 mg/dL.
A1c levels are typically presented as a percentage, but they can also be converted to average blood glucose (sugar) levels, providing patients with a better understanding of their daily fluctuations. For instance, an A1c level of 7% corresponds to an average blood glucose level of approximately 154 mg/dL.
Understanding these levels is crucial as high A1c levels can increase the risk of developing complications associated with diabetes. These include cardiovascular diseases, nerve damage, kidney problems, and eye conditions. Conversely, consistently low A1c levels can indicate the risk of hypoglycemia, commonly known as low blood sugar, which can cause dizziness, confusion, and even loss of consciousness.
Effective Management Strategies
 Managing A1c levels requires a multifaceted approach that combines medication (if prescribed), regular physical activity, a healthy diet, and regular monitoring of blood sugar levels. Monitoring can involve self-testing using portable blood glucose meters and utilizing continuous glucose monitoring systems for real-time tracking.
Managing A1c levels requires a multifaceted approach that combines medication (if prescribed), regular physical activity, a healthy diet, and regular monitoring of blood sugar levels. Monitoring can involve self-testing using portable blood glucose meters and utilizing continuous glucose monitoring systems for real-time tracking.
Adopting a well-balanced, low-glycemic diet plays a crucial role in controlling A1c levels. It is important to consume foods that are low in refined sugars and carbohydrates while incorporating plenty of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Portion control and mindful eating are also essential.
Regular exercise has been found to improve insulin sensitivity, making it easier for cells to utilize blood sugar effectively. Engaging in physical activity for at least 150 minutes every week, as recommended by health professionals, can significantly contribute to achieving and maintaining optimal A1c levels.
Conclusion
 Monitoring A1c levels is an essential part of diabetes management. By maintaining A1c levels within target ranges, individuals can reduce the risk of complications and enjoy a healthier life. However, it is important to note that A1c levels should be monitored in conjunction with regular check-ups and consultation with healthcare professionals to ensure personalized and effective diabetes management.
Monitoring A1c levels is an essential part of diabetes management. By maintaining A1c levels within target ranges, individuals can reduce the risk of complications and enjoy a healthier life. However, it is important to note that A1c levels should be monitored in conjunction with regular check-ups and consultation with healthcare professionals to ensure personalized and effective diabetes management.
Remember, your healthcare team is there to support you in your journey. By working together, you can develop a customized plan that will enable you to maintain optimal A1c levels and lead a fulfilling life despite living with diabetes.